A twisted-pair cable consists of one or more twisted-pair. Each twisted-pair wire usually is color coded for identification. Its wires are twisted together and separately
insulated to each other. They are usually in the form of bundles called cables.
They are installed in building during construction.

Transmission Characteristic:
1. Limited
distance.
2. Limited
Bandwidth of 1 MHz.
3. Limited
data rate of of 100 MHz.
4. Use
both analog (amplifier every 5 km) and digital signals (repeater every 2 km).
5. Susceptible
to interference and noise.
Types of Twisted Pair Cables:
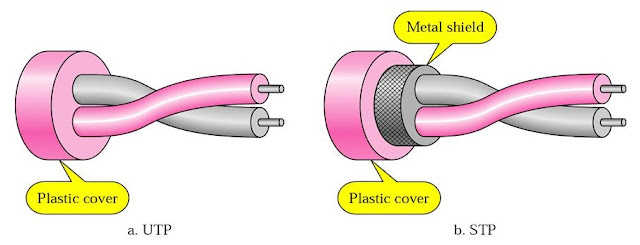
a) Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP): It acts as ordinary telephone wire. It characteristics are: cheapest, easy to install, and suffer
from external interference.
b) Shielded Twisted Pair (STP): It is made up of metal braid that reduces interference.
More expensive, and harder to handle.
Table: UTP Category
 Application of Twisted Pairs:
Application of Twisted Pairs:
UTP Category
|
Data Rate
|
Max. Length
|
Cable Type
|
Applications
|
CAT1
|
1 Mbps
|
-
|
Twisted Pair
|
Old Telephone
Cable
|
CAT2
|
4 Mbps
|
-
|
Twisted Pair
|
Token Ring
Networks
|
CAT3
|
10 Mbps
|
100 m
|
Twisted Pair
|
Token Ring
|
CAT4
|
16 Mbps
|
100 m
|
Twisted Pair
|
Token Ring
|
CAT5
|
100 Mbps
|
100 m
|
Twisted Pair
|
Token Ring,
Ethernet
|
CAT5e
|
1 Gbps
|
100 m
|
Twisted Pair
|
Ethernet, Fast
Ethernet
|
CAT6
|
10 Gbps
|
100 m
|
Twisted Pair
|
Gigabit Ethernet
|
CAT6a
|
10 Gbps
|
100 m
|
Twisted Pair
|
Gigabit Ethernet
|
CAT7
|
10 Gbps
|
100 m
|
Twisted Pair
|
Gigabit Ethernet
|
 Application of Twisted Pairs:
Application of Twisted Pairs:
1. They
are used in telephone networks between house and local exchange called
Subscriber Loop.
2. Within
buildings.
3. For
private branch exchange.
4. Local
area networks.
Pros and Cons:
1. Easy
to work with
2. Short
range
3. Low
data rate