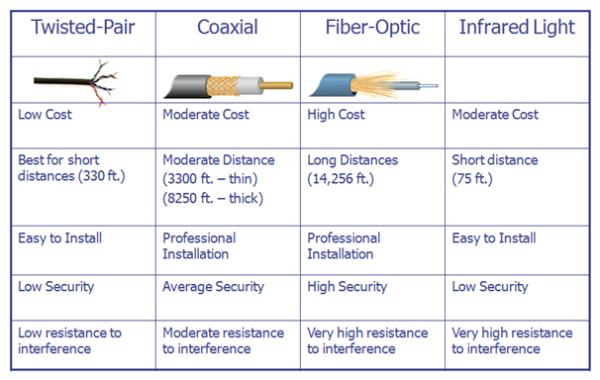
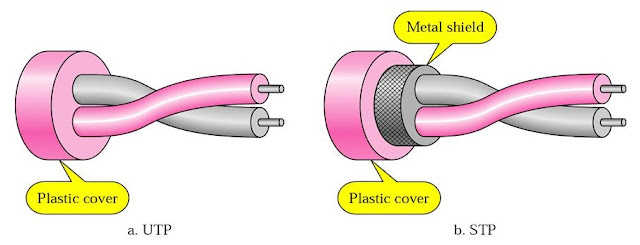
Basic Concept & Basic Laws
Charge of electron is 1.602*10-19
C.
3) Voltage: The
energy required to move a unit charge through an element, measured in volts (V)
is called voltage.
4)
Power: This
is the time rate of expending or absorbing energy, measured in watts (W),
mathematically,

Plus Sign: Power is absorbed by the element (resistor,
inductor).
Minus Sign: Power is supplied by the element (battery,
generator).
If the current enters through the positive polarity
of the voltage, then element is absorbing power.
If the current enters through the negative polarity of the voltage, then element is delivering power.
If the current enters through the negative polarity of the voltage, then element is delivering power.